Multomodal deep learning - CMU 강의 1.1 Intro
in Deep Learning on Multimodal
강의 1.1 Intro에 대한 내용 정리.
What is Multimodal
수학적인 정의보다 ‘감각’과 관련됨.
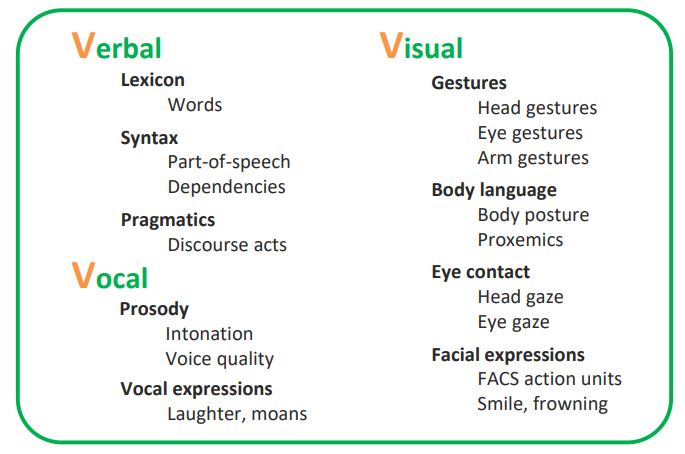
인간은 3가지 언어로 ‘소통’ 한다.
- ‘내용언어’(Verbal) = 전달하고자 내용
- ‘시각언어’(Visual) = 보이는 언어로서 표정이나 태도
- ‘청각언어’(Vocal) = 들리는 언어로서 음성, 강약, 어투, 어속, 발음 => 이 3가지 중 1개만 사용하는 것이 아니라, 복합적으로 사용함.
Modality
- 정의 : The way in which something happens or is experienced.
- (논문과 강의에서는 주로 감각적인 Modality(촉감, 시각, 청각 등)를 말한다.)
- 예시 : 1. Text로 주어진 자연어, 2. 음성으로 주어진 자연어 or 음악, 3. 이미지 or 비디오, 4. MRI or 적외선 사진 등
- 이 강의에서는 Natural language, Visual, Auditory에 초점을 맞춘다.
Historical view
- 심리학 분야에서 early work가 있었고, 딥러닝 분야에서는 2010년부터 연구되었다.
- ‘Representation learning’ (a.k.a deep learning) 에서 가능했던 이유
- New large-scale multimodal datasets
- Faster computer and GPUS
- High-level visual features => CNN의 등장으로 High dimensional representation을 take 할 수 있음.
- “Dimensional” linguistic features => 단어를 vector로 표현하는 등, useful한 representation 가능 +) 모달리티들은 서로가 상당히 비슷한 특징을 가지고 있음. noise를 예로 들면, 이미지에서의 noise는 pixcel 단위로 튀는? 느낌이고, 자연어처리에서의 noise는 오탈자라고 볼 수 있음.
정확하게 ‘같은’ space에 놓여있지는 않지만 싱딩히 비슷함. 따라서 heterogeneous한 관계임.
이러한 특징은 ‘딥러닝’을 적용시키기에 적합함.
- 관련 논문
- Multimodal deep learning [ICML 2011]
- Multimodal Learning with Deep Boltzmann Machines [NIPS 2012]
- Visual attention: Show, Attend and Tell: Neural Image Caption Generation with Visual Attention [ICML 2015]
- Multimodal deep learning [ICML 2011]
Core Technical Challenges
- 이에 대한 근거는 Tadas Baltrusaitis, Chaitanya Ahuja, and Louis-Philippe Morency 이 작성한 Multimodal Machine Learning: A Survey and Taxonomy.를 바탕으로 함.
- Representation
- Alignment
- Fusion
- Translation
- Co-Learning
- Representation
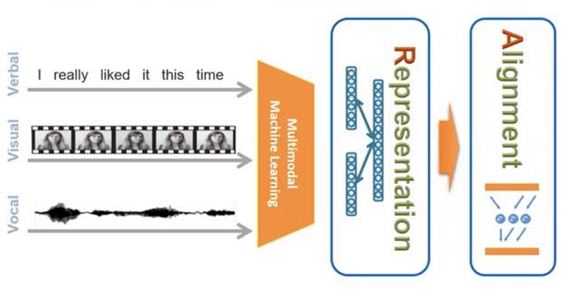
+) 추가 설명 사진
- Representation과 Alignment라는 용어가 어색할 때 위 그림을 참고해서 이해하시길…
Core Challenge 1 - Representation
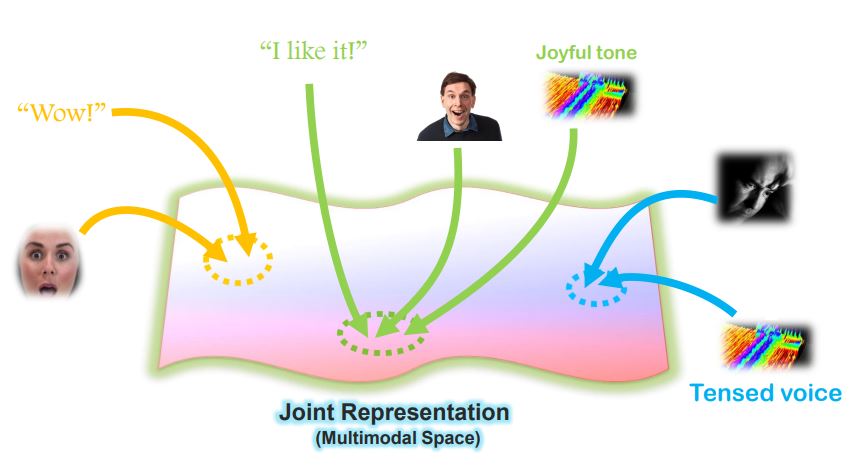
- “I like it!”, 행복한 표정과 말투 등은 어떤 공간에 유사하게 Encode될 것임.
- 이러한 Multimodal Vector Space에서의 연산을 잘 다루는 것이 중요함.
- 정의 : Learning how to represent and summarize multimodal data in away that exploits the complementarity and redundancy.
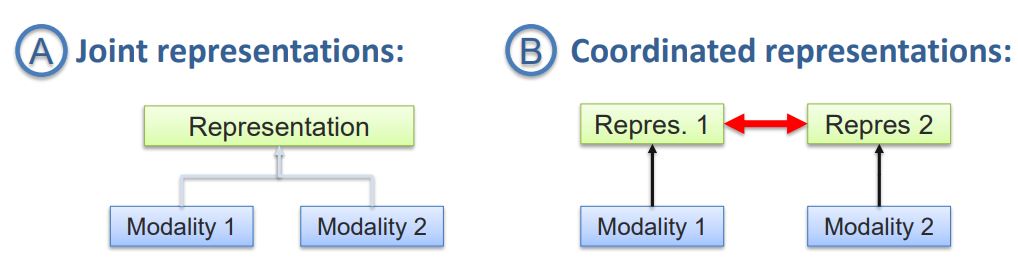
- 이러한 Representation은 2 가지 종류가 있음. 하나는 Joint representations이고 나머지 하나는 Coordinated representations임.
- 많은 사람들은 멀티모달에 대한 설명을 들으면, 왼쪽 그림의 Joint representations을 생각했을 것.
- 두 개의 Modality가 있을때, 이 둘을 합쳐서 한 개의 vector space를 갖는 Representation으로 나타내는 것을 의미
- 두 개의 Modality를 합치는 것이 아니라 그들 각각의 space를 갖는 Representation을 구해서 sub space를 만든 후 스팩트럼처럼 조정할 수 있음.
- Ex, 언어적 표현과 시각적 표현을 따로 구해서 동일선상의 space로 조정해줌. CCA(canonical correlation analysis) 적용.
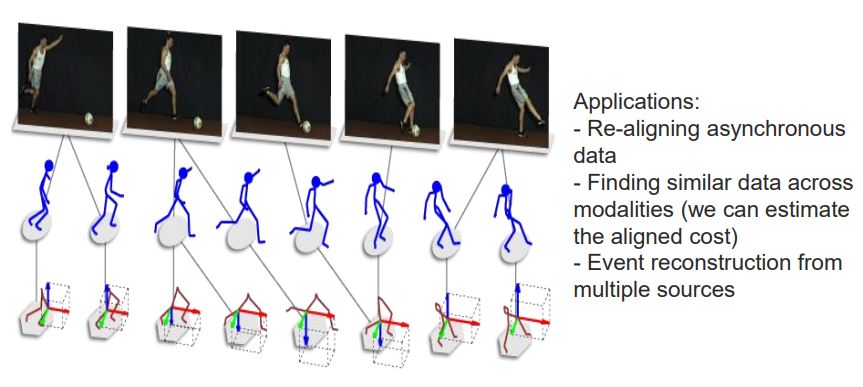
Core Challenge 2 - Alignment
- 정의 : Identify the direct relations between (sub)elements from two or more different modalities.
- synchronize하는 것. 말하는 것(음성, 입 모양, 의미 등)과 제스쳐를 동시에 하기 때문에 이러한 modalities를 정렬하는 것이 필요함.
- 이러한 Alignment는 2 가지 종류가 있음. 하나는 Explicit Alignment이고 나머지 하나는 Implicit Alignment임.
- Explicit Alignment는 우리의 목적, loss function, task가 같이 align 되어 있는 것. (내가 optimizing 하고 싶은 loss function이 alignment 될 예정일 때)
(EX. 요리하는 동영상에 요리 레시피에 대한 step을 align 해주는 것)
- 대부분의 Alignment는 ‘intermediate step’에 불과함. real loss function은 아마 another task일 것.
- Implicit Alignment는 latent alignment를 이용함. attention model - self attention, transformers 등
- 이미지에 있는 every words, every objects, every possible things를 align 하는 task에서 alignment는 explicit가 아니라 언어 ‘생성’이고 latent state를 이용한다.
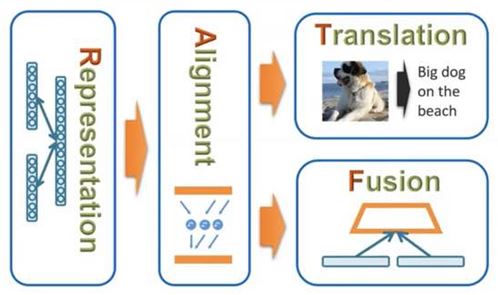
Translation과 Fusion의 Branch
- Multimodal task 과정에서 Representation과 Alignment는 거의 무조건 사용하지만, Alignment 이후에 Translation과 Fusion이라는 Branch가 생긴다. 즉, 어떤 task인지에 따라 갈리게 된다.
- 갈라지는 두 개의 과정은 loss function이 뭔지에 따라 달라진다.
- Translation은 한 modality에서 다른 modality로 translating(maping) 하는 것을 의미.
- (Ex. 이미지 캡셔닝-image to text)
- Fusion은 모든 modalities를 합쳐서 something else(high level)를 추론하는 것을 의미.
- (Ex. 감정 분석이나 비디오에서 event를 검출하는 것 등)
Core Challenge 3 - Translation
- 정의 : Process of changing data from one modality to another, where the translation relationship can often be open-ended or subjective.
- 한 modality에서 다른 modality로 데이터를 바꾸는 과정뿐만 아니라 연결상태는 유지함을 의미.
- (Ex. language to language, speech generation)
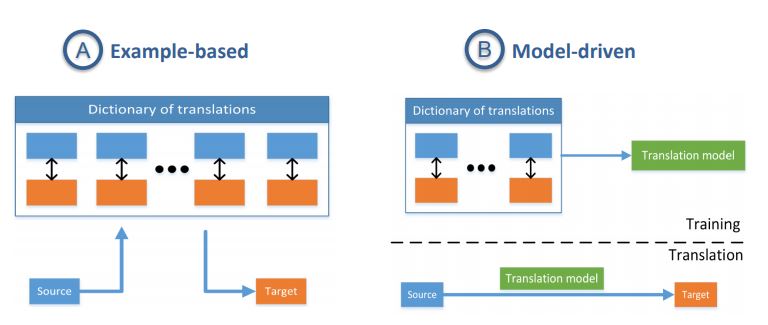
- 이러한 Translation은 2 가지 종류가 있음. 하나는 Example-based 이고 나머지 하나는 Model-driven 임.
- Example-based는 non-parametric한 접근법(Ex. k-nearest neighbor)이고, Model-driven은 parametric한 접근법(Ex. 생성 모델)임.
Core Challenge 4 - Fusion
- 정의 : To join information from two or more modalities to perform a prediction task.
- 오래전부터 연구된 분야임. Modality를 어떻게 통합시킬지에 대한 과제
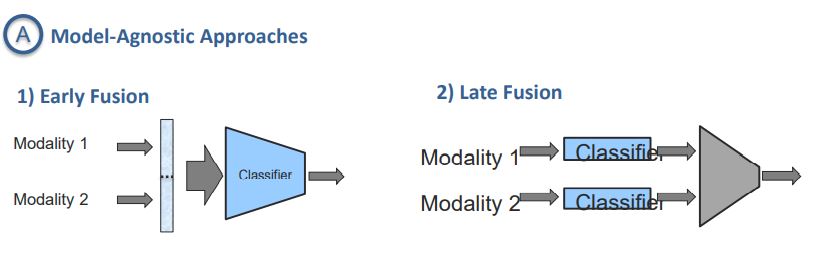
- 이러한 Fusion은 2 가지 종류가 있음. 하나는 Model-Agnostic Approaches 이고 나머지 하나는 Model-Based (Intermediate) Approaches 임.
- Model-Agnostic Approaches 속에서도 2가지 종류가 있음. Early Fusion과 Late Fusion임.
- Model-Agnostic Approaches는 old한 방법.
- Early Fusion은 모델 초반 부에 Modalities의 특징맵을 concatenated하기 때문에 low level multimodal 문제를 해결할 때 사용한다.
- Late Fusion은 fusion전에 각각의 Modality를 internally하게 processing하기 때문에 high level feature를 얻을 수 있고 이를 통해 모델을 구성한다.
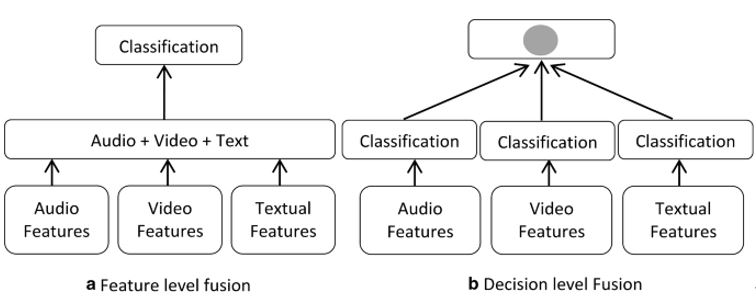
또한 Early Fusion은 “Feature level fusion”이라고 불리며, Late Fusion은 “Decision level Fusion”이라고 불린다.
- Model-Based (Intermediate) Approaches는 최근에 많이 사용되는 접근법
- Deep neural networks, Kernel-based methods, Graphical models가 있음.
- 신경망 아키텍처는 멀티모달 표현 구성 요소와 융합 구성 요소 모두에 대한 End-to-End 학습을 허용
- 신경망 접근 방식의 주요 단점은 해석성이 부족하다는 것과 대규모 학습 데이터 세트가 필요하다는 것임.
Core Challenge 5 - Co-Learning
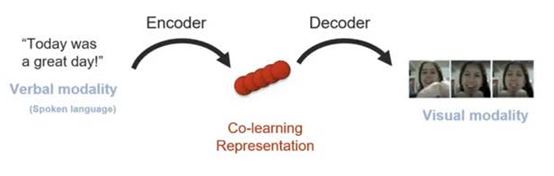
- 정의 : Transfer knowledge between modalities, including their representations and predictive models.
- 단일 모달 task의 모델 훈련 시점에서, 다른 Modality가 현제 해결하고자 하는 문제의 Modality를 도와주는 것을 의미.
- 이러한 Co-Learning은 데이터의 양이 제한되어 있거나, 아직 annotated가 안됐을 때 유용하게 활용할 수 있다.
- (Ex. language could help vision but vision could also help language.)
- Co-Learning에서 직면한 과제는 이렇게 한 Modality가 다른 Modality를 도와줄 때, “서로 pairing이 얼마나 strong하게 됐느냐?” 이다.(특히 언어 번역 분야)
- intermediate representation을 사용하여 source로 부터 target을 생성하고, sentimentic space의 사용으로 보이지 않는(훈련 데이터에 없는 인스턴스) 단어(이미지 혹은 해결하고자 하는 task의 target)을 예측할 수 있음.
이는 Zero Shot Learning이 가능하다는 것을 의미함.
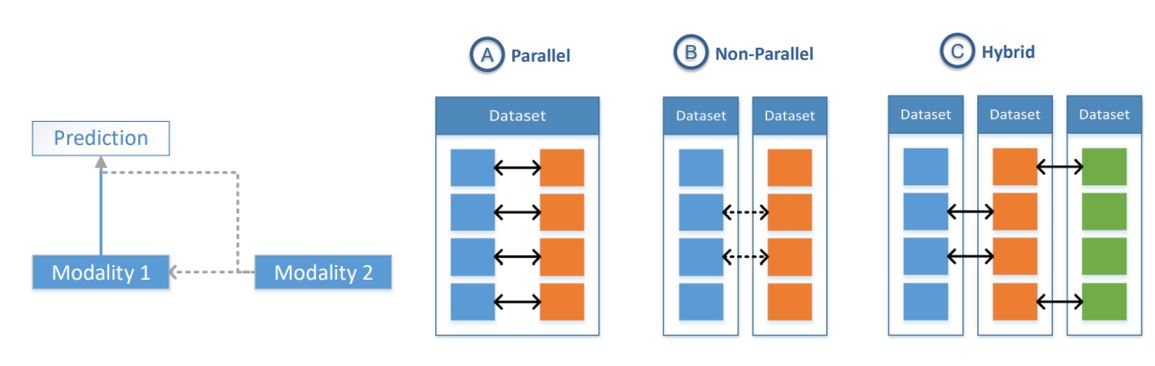
- parallel과 non-parallel은 추후 보충.
- parallel — modality은 동일한 데이터 세트에서 가져오고 인스턴스간에 직접적인 대응이 있음.
- Non parallel — modality는 서로 다른 데이터 세트에서 나왔으며 중복되는 인스턴스가 없지만, 일반적인 범주 또는 개념에서 중복됨.
이상 Intro 리뷰 끝. 놀랍게도 20페이지 서베이 논문을 1시간 반 만에 요약 강의해주심.